Demystifying CORS in Web Development
I remember the first time I encountered a CORS error—it was frustrating, blocking my web app from fetching data seamlessly. In this story, I'll share how I learned about cross-origin resource sharing, why it's crucial for security, and practical ways to handle it, turning potential roadblocks into smooth sailing.
TL;DR
I once faced CORS errors fetching data across servers, revealing the need for browser security rules to prevent data theft.
Exploring the same origin policy, I discovered how it restricts requests and introduces CORS headers for safe access.
Simple requests worked easily with basic methods, but complex ones required a pre-flight check, adding an extra layer of verification.
To fix issues, I configured servers in Node.js or Spring Boot, and used extensions for quick development fixes.
Understanding CORS versus CSRF highlighted broader security, leaving me eager to learn more prevention strategies.
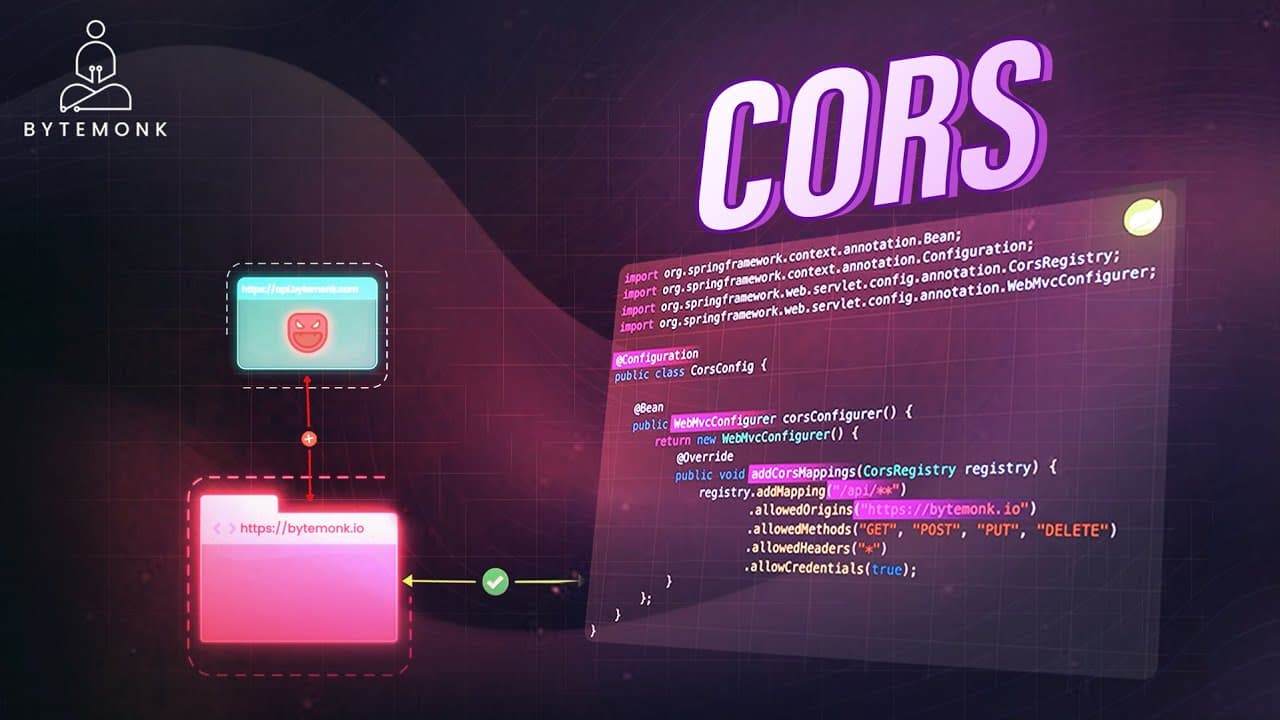
When I first built a web app that needed to fetch data from another server, I hit a wall with CORS errors. I realized it stemmed from the browser's same origin policy, a rule designed to protect users by blocking requests between different domains, protocols, or ports. For instance, if my front end was on https://bank.io, it couldn't just reach out to https://api.example.com without proper permissions, as that could let malicious sites steal sensitive data like banking information.

This policy made sense once I dug deeper; it prevents scenarios where a hacker site could impersonate me on a legitimate site. CORS steps in as the solution, using HTTP headers to allow controlled access. In my experience, when my browser sends a request from one origin to another, it includes an Origin header, and the server responds with Access-Control-Allow-Origin if it approves.
If the server doesn't respond correctly, I get that dreaded error, but understanding simple versus pre-flight requests helped clarify things. A simple request, like a GET with standard headers, goes through directly if allowed, but anything more complex—such as using PUT, custom headers, or non-standard content types—triggers a pre-flight OPTIONS request first. This pre-flight acts as a permission check, ensuring the server consents before the real request proceeds.

To handle these in practice, I configured my server. In Node.js, I used middleware to set Access-Control-Allow-Origin for specific domains, making it straightforward to enable CORS. For Java with Spring Boot, I created a configuration class that defined policies, specifying allowed origins, methods, and headers while enabling credentials for secure sessions.
Even if I couldn't access the backend, I found workarounds like using a proxy to make requests appear from the same origin or installing browser extensions for testing. These tools were lifesavers during development, letting me bypass restrictions temporarily without altering the server. I always remembered to use them only in non-production environments to maintain security.

One key insight I gained was distinguishing CORS from CSRF; while CORS manages which sites can access APIs, CSRF involves tricking authenticated users into unwanted actions. This realization prompted me to prioritize comprehensive security measures in my projects.
Reflecting on this journey, mastering CORS not only resolved my immediate issues but also deepened my appreciation for web security, paving the way for more robust applications. Looking ahead, I'll continue exploring related topics to build even safer systems.
Key Takeaways
The same origin policy prevents unauthorized data access, making CORS essential for secure cross-origin requests.
Simple requests proceed if allowed, while pre-flight requests handle more complex scenarios with preliminary checks.
Configuring servers with proper headers or using development tools can effectively manage and resolve CORS errors.